Optimize code
The optimize code feature of JDroid enhances the performance of your code by reducing the memory usage and optimizing the execution speed. However, optimizing the code with JDroid does not necessarily shorten its length. It only focuses on improving execution speed and reducing memory allocation. You can use this feature across all the 88 languages our platform supports. Note : The ‘optimize code’ feature usesone AI credit. The JDroid API server also supports the ‘optimize code’ feature. For more information, refer to the JDroid API server documentation. Please refer to this documentation to know the prerequisites for using JDroid AI.
Where can I find the ‘optimize code ’ feature?
You’ll find the ‘optimize code’ feature within the JDroid box on the right-hand side of the IDE. 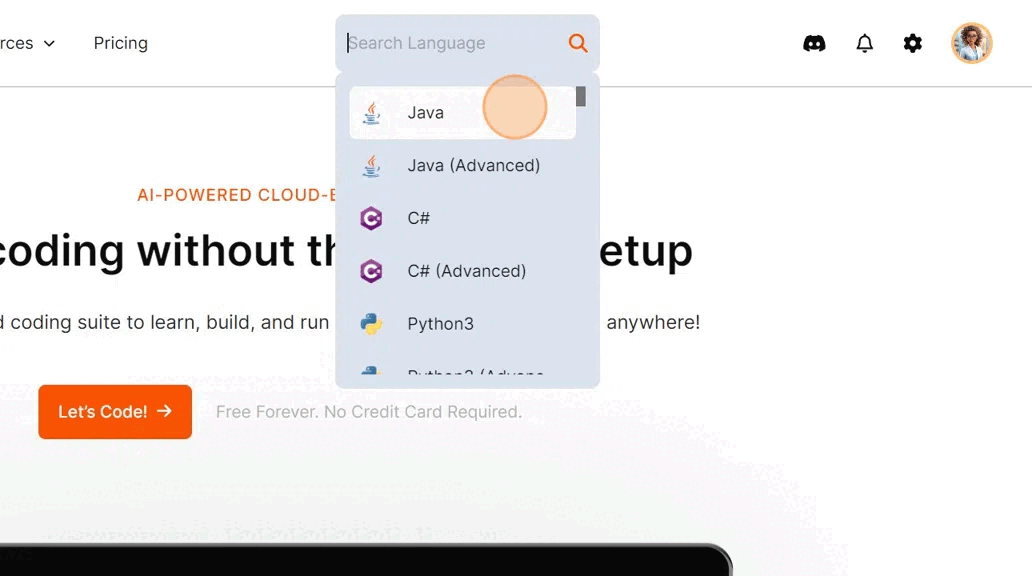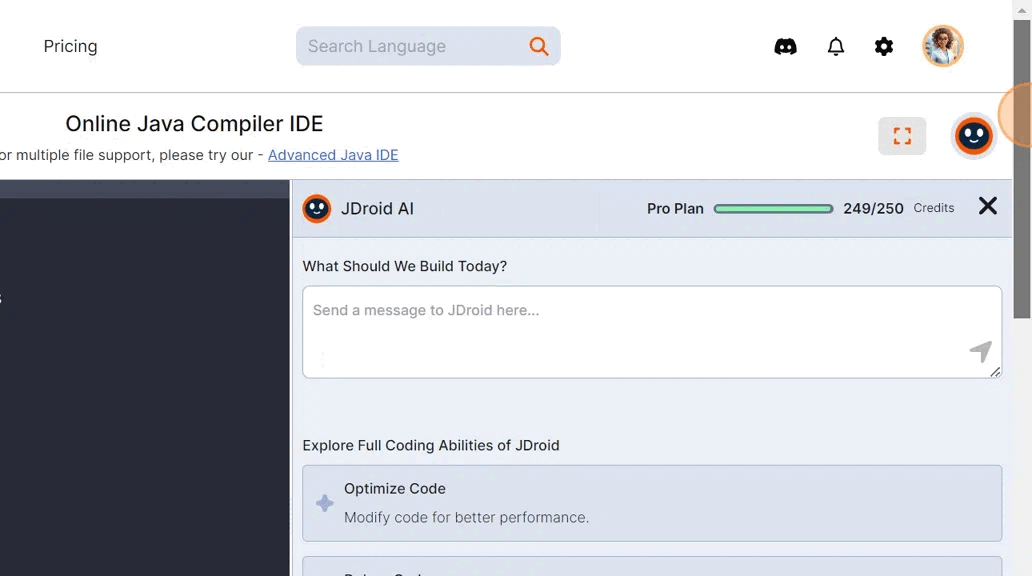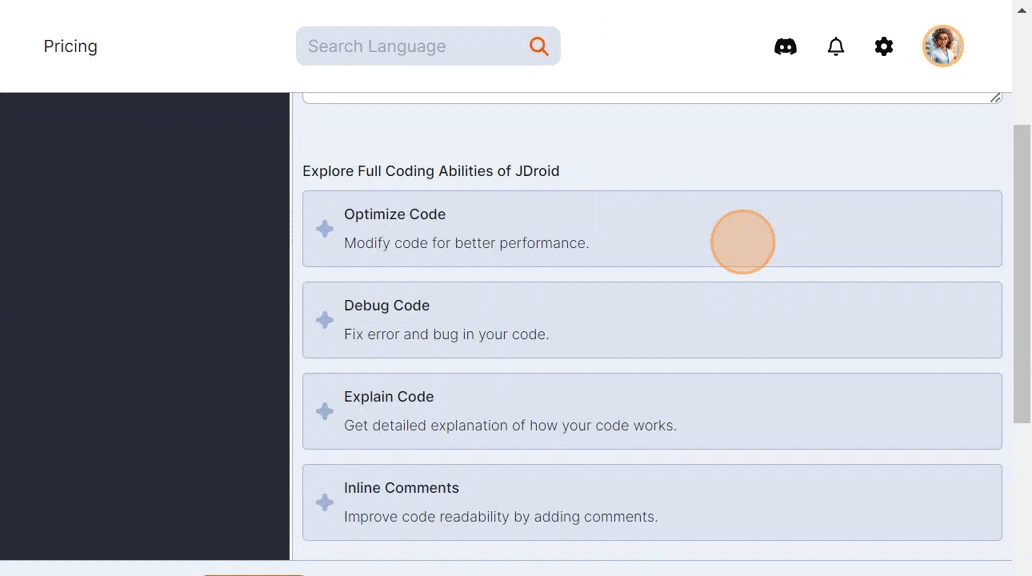
Important note:
When you opt for the optimize code feature, it will only **optimize the code in the IDE. ** If you need to optimize a different code snippet, save the code you have in the IDE, paste the new snippet you wish to optimize in the code editor, and select the optimize code option. Refer to this documentation to understand how to save your code in the IDE.
How ‘optimize code ’ works?
As explained above, optimizing your code with JDroid AI helps it perform better with faster execution and less memory space. We’re using a sample template code on simple addition on the JAVA compiler IDE to show how optimizing code works. Here’s the sample template to try:
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x=10;
int y=25;
int z=x+y;
System.out.println("Sum of x+y = " + z);
}
}
You can simply select the language you wish to code in, write your code, or generate a code using JDroid, and then select the optimize code option. To understand how the generate new code feature works, read this documentation. If you generate code using JDroid, please paste the code into the IDE so you don’t waste credits or encounter errors.  Here’s the output given by JDroid:
Here’s the output given by JDroid:
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Sum of x+y = " + (10+25));
}
}
Example prompts to try
Here are sample code snippets you can use to optimize it using JDroid. The samples provided are in JAVA, so you must use the JAVA IDE.
Sample code that checks if a number is prime
public class PrimeNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int limit = 100; // Set the limit to the maximum number you want to check for primality
System.out.println("Prime numbers between 1 and " + limit + " are:");
// Iterate over all numbers from 2 to the specified limit
for (int number = 2; number <= limit; number++) {
if (isPrime(number)) {
System.out.println(number);
}
}
}
// Method to check if a number is prime
public static boolean isPrime(int num) {
// Check for numbers less than 2 and even numbers greater than 2
if (num <= 1 || (num % 2 == 0 && num != 2)) {
return False;
}
// Check for divisibility up to the square root of the number
for (int i = 3; i <= Math.sqrt(num); i += 2) {
if (num % i == 0) {
return False;
}
}
return True;
}
}
Sample code to perform Bubble Sort in an array
public class BubbleSortExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90};
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println("Sorted array:");
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
}
// Method to perform bubble sort
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
boolean swapped;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
swapped = False;
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// swap arr[j] and arr[j + 1]
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = True;
}
}
// If no two elements were swapped by inner loop, then break
if (!swapped)
break;
}
}
}
Sample guessing game code
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GuessingGame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random rand = new Random();
int numberToGuess = rand.nextInt(100) + 1;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("I'm thinking of a number between 1 and 100. Can you guess what it is?");
while (True) {
int guess = scanner.nextInt();
if (guess < numberToGuess) {
System.out.println("Too low, try again!");
} else if (guess > numberToGuess) {
System.out.println("Too high, try again!");
} else {
System.out.println("Congratulations! You guessed the number!");
break;
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}
Things to consider while using optimize code
JDroid AI is still learning and can produce an error code, especially if:
- The code you wish to optimize is not pasted in the IDE
- You’re using complex or new languages like Befunge,Cow,Brainfuck,Intercal, etc.
- The code you ask it to optimize is very complex.
Spotted a bug?
If you find any issues with our ‘optimize code’ feature or need more help, please fill out this form or drop an email to hello@jdoodle.com. Our support team will respond at the earliest.
