Adding libraries & dependencies
Enhance your coding with external libraries.
JDoodle provides library support for 20 languages. Below is a comprehensive guide on how to add libraries for each supported language, including the package managers used and example libraries. 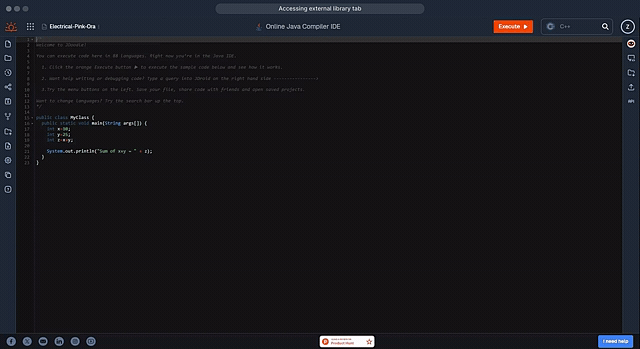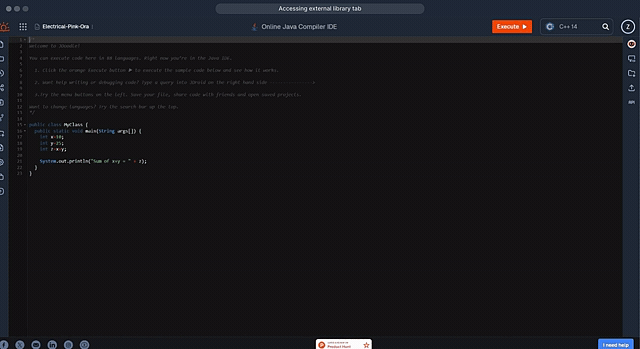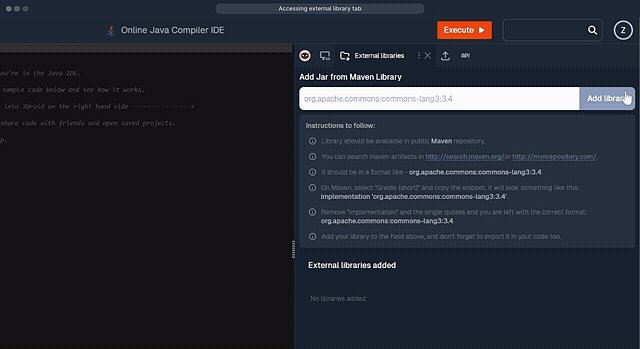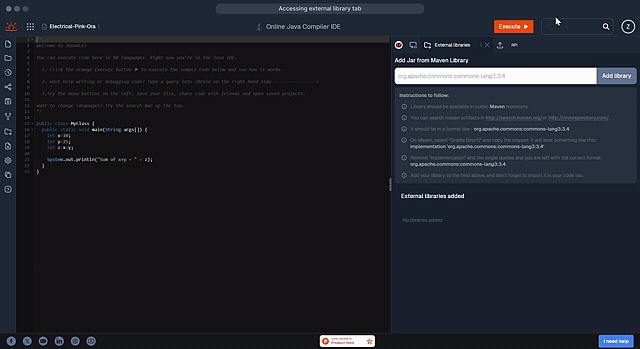
The table below summarizes the languages, their package managers, and example libraries.
| Language | Package Manager | Example Libraries |
|---|---|---|
| C# | NuGet | Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3 |
| Node.js | NPM | lodash:4.17.21 |
| Java (Maven) | Maven | org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.4 |
| Kotlin / Scala | JAR Libraries | Specify JAR files |
| C | Arch Linux (pacman) | boost |
| Python | pip | pandas |
| C++ (14/17) | Arch Linux (pacman) | boost |
| C99 | Arch Linux (pacman) | gsl |
| TypeScript | NPM | @types/lodash:4.14.202 |
| PHP | Composer (Packagist) | markrogoyski/math-php:2.* |
| Lua | LuaRocks | lua-zlib |
| Swift | Package.swift | SwiftDate |
| Bash | Arch Linux (pacman) | jq |
| Dart | Pub.dev | advance_math |
| Ruby | RubyGems | faker:2.18.0 |
| Perl | CPAN | Date::Time@1.65 |
| R | CRAN | dplyr |
| VB.NET | NuGet | Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3 |
| Prolog | SWI-Prolog Library | matrix |
C#
JDoodle supports adding libraries for C# using the NuGet package manager. For example, you can add libraries like Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3, EntityFramework:6.4.4, or NUnit:3.13.2. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for your desired library on NuGet, ensuring it’s available in the public repository.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName:Version. For example:
- Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3
- EntityFramework:6.4.4
- Add the Library: In JDoodle, input the library information in the library field provided.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use the using directive to include the library in your code.
Example code:
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var obj = new { Name = "JDoodle", Feature = "Library Support" };
string json = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(obj);
Console.WriteLine(json);
}
}
Node.js
JDoodle allows adding libraries for Node.js using NPM. Examples include lodash:4.17.21, axios:0.21.1, and express:4.17.1. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for the library on NPM.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName:Version, such as:
- lodash:4.17.21
- axios:0.21.1
- Add the Library: Enter the library name and version in JDoodle’s library field.
- Require the Library in Your Code: Use require() to include the library.
Example Code:
const axios = require('axios');
axios.get('https://api.jdoodle.com')
.then(response => {
console.log('Status Code:', response.status);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
Groovy
JDoodle supports adding libraries for Groovy using Maven. For example, you can add org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0 or org.jsoup:jsoup:1.14.2. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for the library on Maven Repository.
- Specify the Library: Use the format
: : , like: - org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0
- org.jsoup:jsoup:1.14.2
- Add the Library: Input the library details in the JDoodle library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use @Grab to include the library.
Example Code:
@Grab('org.jsoup:jsoup:1.14.2')
import org.jsoup.Jsoup
def doc = Jsoup.connect('https://www.jdoodle.com').get()
println(doc.title())
Kotlin/Scala
For Kotlin and Scala, JDoodle allows adding JAR libraries. Examples include kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.5.2 for Kotlin and com.typesafe.play:play-json_2.13:2.9.2 for Scala. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for the required JAR files in public repositories like Maven Repository.
- Specify the Library: Provide the library details in JDoodle’s library field, for example:
- Kotlin: org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.5.2
- Scala: com.typesafe.play:play-json_2.13:2.9.2
- Add the Library: Ensure the library is properly referenced in the library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use the appropriate import statements.
Example Code (Kotlin):
import kotlinx.coroutines.*
fun main() = runBlocking {
launch {
delay(1000L)
println("World!")
}
println("Hello,")
}
C
JDoodle supports adding libraries for C from the Arch Linux package repository using pacman. Examples include gsl and openssl. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for the library on the Arch Linux Packages.
- Specify the Library: Use the exact package name, such as:
- gsl
- openssl
- Add the Library: Input the package name in the JDoodle library field.
- Include the Library in Your Code: Use #include directives to include headers.
Example Code:
#include <openssl/sha.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
unsigned char digest[SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH];
const char *str = "JDoodle";
SHA256((unsigned char*)&str, strlen(str), (unsigned char*)&digest);
printf("SHA256 digest: ");
for(int i = 0; i < SHA256_DIGEST_LENGTH; i++)
printf("%02x", digest[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Python 2/Python 3
JDoodle allows adding libraries for Python using pip. Examples include requests, numpy, and matplotlib. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search for the library on PyPI.
- Specify the Library: Use the library name, such as:
- requests
- matplotlib
- Add the Library: Input the library name in the JDoodle library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use import statements as usual.
Example Code:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])
plt.title('Simple Plot')
plt.show()
Here’s an example project using Pandas: https://www.jdoodle.com/ga/3%2FJvz9z0P8QekGQEIjHnjg%3D%3D
C++, C++14, C++17
JDoodle supports adding libraries for C++ from the Arch Linux package repository using pacman. Examples include boost and openssl. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on Arch Linux Packages.
- Specify the Library: Use the package name, for example:
- boost
- openssl
- Add the Library: Input the package name in the JDoodle library field.
- Include the Library in Your Code: Use #include directives.
Example Code:
#include <boost/algorithm/string.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::string str = "Boost C++ Libraries";
std::vector<std::string> results;
boost::split(results, str, boost::is_any_of(" "));
for(const auto& s : results) {
std::cout << s << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
C99
JDoodle supports adding libraries for C99 from the Arch Linux package repository using pacman. An example library is gsl. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on Arch Linux Packages.
- Specify the Library: Use the package name, such as gsl.
- Add the Library: Input the package name in the JDoodle library field.
- Include the Library in Your Code: Use #include directives.
Example Code:
#include <gsl/gsl_sf_gamma.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
double x = 5.0;
double y = gsl_sf_gamma(x);
printf("Gamma(%g) = %.18e\n", x, y);
return 0;
}
TypeScript
JDoodle allows adding libraries for TypeScript using NPM. Examples include @types/lodash:4.14.202 and axios:0.21.1. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on NPM.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName:Version, like:
- @types/lodash:4.14.202
- axios:0.21.1
- Add the Library: Input the library and version in JDoodle’s library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use import statements.
Example Code:
import axios from 'axios';
axios.get('https://api.jdoodle.com')
.then(response => {
console.log('Status Code:', response.status);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
PHP
JDoodle supports adding libraries for PHP using Composer (Packagist). Examples include guzzlehttp/guzzle:7.3.0 and monolog/monolog:2.3.5. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on Packagist.
- Specify the Library: Use the format vendor/package:version, such as:
- guzzlehttp/guzzle:7.3.0
- monolog/monolog:2.3.5
- Add the Library: Input require vendor/package:version in JDoodle’s library field.
- Include the Composer Autoloader in Your Code: Use require ‘vendor/autoload.php’;.
Example Code:
<?php
require 'vendor/autoload.php';
use GuzzleHttp\Client;
$client = new Client();
$response = $client->request('GET', 'https://api.jdoodle.com');
echo 'Status Code: ' . $response->getStatusCode();
Lua
JDoodle allows adding libraries for Lua using LuaRocks. Examples include lua-zlib and luasocket. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on LuaRocks.
- Specify the Library: Use the library name, for instance:
- lua-zlib
- luasocket
- Add the Library: Input the library name in the JDoodle library field.
- Require the Library in Your Code: Use require.
Example Code:
local socket = require 'socket'
local time = socket.gettime()
print('Current Time:', time)
Swift
JDoodle supports adding libraries for Swift by updating the Package.swift file in your project directory. An example is adding the SwiftDate library. Instructions: Update Package.swift: Modify your Package.swift file to include the desired library.
// swift-tools-version:5.5
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "jdoodle",
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/SwiftDate/SwiftDate.git", from: "6.3.1")
],
targets: [
.executableTarget(
name: "jdoodle",
dependencies: ["SwiftDate"],
path: "."
),
]
)
Import the Library in Your Code: Use the import statement to include the library. Example Code:
import SwiftDate
let now = Date()
let formattedDate = now.toFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
print("Current Date and Time:", formattedDate)
Bash
JDoodle allows adding utilities for Bash from the Arch Linux package repository using pacman. Examples include jq and curl. Instructions:
- Find the Utility: Search on Arch Linux Packages.
- Specify the Utility: Use the package name, like:
- jq
- curl
- Add the Utility: Input the utility name in the JDoodle library field.
- Use the Utility in Your Script: Call the utility as you would in a shell script.
Example Code:
#!/bin/bash
curl -s 'https://api.jdoodle.com' | jq '.'
Dart
JDoodle supports adding libraries for Dart using Pub.dev. Examples include advance_math and http. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on Pub.dev.
- Specify the Library: Use the package name, such as:
- advance_math
- http
- Add the Library: Input the package name in the JDoodle library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use import statements.
Example Code:
import 'package:advance_math/advance_math.dart';
void main() {
var result = AdvancedMath.factorial(5);
print('Factorial of 5 is $result');
}
Ruby
JDoodle allows adding libraries for Ruby using RubyGems. Examples include faker:2.18.0 and httparty:0.18.1. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on RubyGems.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName:Version, for example:
- faker:2.18.0
- httparty:0.18.1
- Add the Library: Input the library name and version in the JDoodle library field.
- Require the Library in Your Code: Use require.
Example Code
require 'faker'
puts Faker::Name.name
Perl
JDoodle supports adding libraries for Perl from CPAN. Examples include DateTime@1.65 and LWP::UserAgent@6.52. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on MetaCPAN.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName@Version, such as:
- DateTime@1.65
- LWP::UserAgent@6.52
- Add the Library: Input the library name and version in the JDoodle library field.
- Use the Library in Your Code: Use use statements.
Example Code:
use DateTime;
my $dt = DateTime->now;
print "Current Date and Time: " . $dt->datetime . "\n";
R
JDoodle allows adding libraries for R from CRAN. Examples include dplyr and ggplot2. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on CRAN.
- Specify the Library: Use the library name, for instance:
- dplyr
- ggplot2
- Add the Library: Input the library name in the JDoodle library field.
- Load the Library in Your Script: Use library().
Example Code
library(dplyr)
data <- mtcars
filtered_data <- filter(data, cyl == 6)
print(filtered_data)
VB.NET
JDoodle supports adding libraries for VB.NET using NuGet. Examples include Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3 and NUnit:3.13.2. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on NuGet.
- Specify the Library: Use the format LibraryName:Version, like:
- Newtonsoft.Json:13.0.3
- NUnit:3.13.2
- Add the Library: Input the library in the JDoodle library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use Imports.
Example Code:
Imports Newtonsoft.Json
Module Program
Sub Main()
Dim obj = New With {.Name = "JDoodle", .Feature = "Library Support"}
Dim json As String = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(obj)
Console.WriteLine(json)
End Sub
End Module
Prolog
JDoodle allows adding libraries for Prolog from SWI-Prolog’s built-in libraries. Examples include matrix and lists. Instructions:
- Identify the Library: Ensure the library is available in SWI-Prolog’s standard library.
- Specify the Library: Use the library name, such as matrix.
- Add the Library: Input the library name in the JDoodle library field.
- Use the Library in Your Code: Include the module using :- use_module(library(library_name))..
Example Code:
:- use_module(library(lists)).
main :-
flatten([1,[2,3],[4,[5]]], FlatList),
writeln(FlatList).
Java
JDoodle supports adding libraries for Java using Maven. Examples include org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0 and com.google.guava:guava:30.1.1-jre. Instructions:
- Find the Library: Search on Maven Repository.
- Specify the Library: Use the format groupId:artifactId:version, for example:
- org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.12.0
- com.google.guava:guava:30.1.1-jre
- Add the Library: Input the library in the JDoodle library field.
- Import the Library in Your Code: Use import statements as needed.
Example Code:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String reversed = StringUtils.reverse("JDoodle");
System.out.println("Reversed String: " + reversed);
}
}
Here’s an example project using Jsoup: https://www.jdoodle.com/ga/ukBOpmW9ymgwMVCJSkut7A%3D%3D
General guidelines
- Always ensure the library is available in the specified package repository.
- Use the exact library name and version as listed in the repository.
- Import or include the library in your code as per the language’s syntax.
- For languages like Swift, update the project configuration files as instructed.
- If a library requires special installation steps, follow the instructions provided in the repository or the library’s documentation.
