Explain code
The explain code feature of JDroid AI provides a detailed description of your code logic and also explains the errors if your code has syntax or logic errors. You can use it across all the 88 languages our platform supports. This feature is useful for students to understand the working logic behind a code snippet and for educators looking to draft quick and descriptive code explanations. Note : The explain code feature usesone AI credit. However, if you debug the code and it provides an explanation, it will also cost only one AI credit. Our JDroid API also supports the explain code feature. For more information, refer to the JDroid API server documentation. If you wish to know the requirements for using the explain code feature of JDroid AI, please refer to this documentation.
Where can I find the ‘explain code ’ feature?
The ‘explain code’ feature is located within the JDroid box on the right side of the IDE. 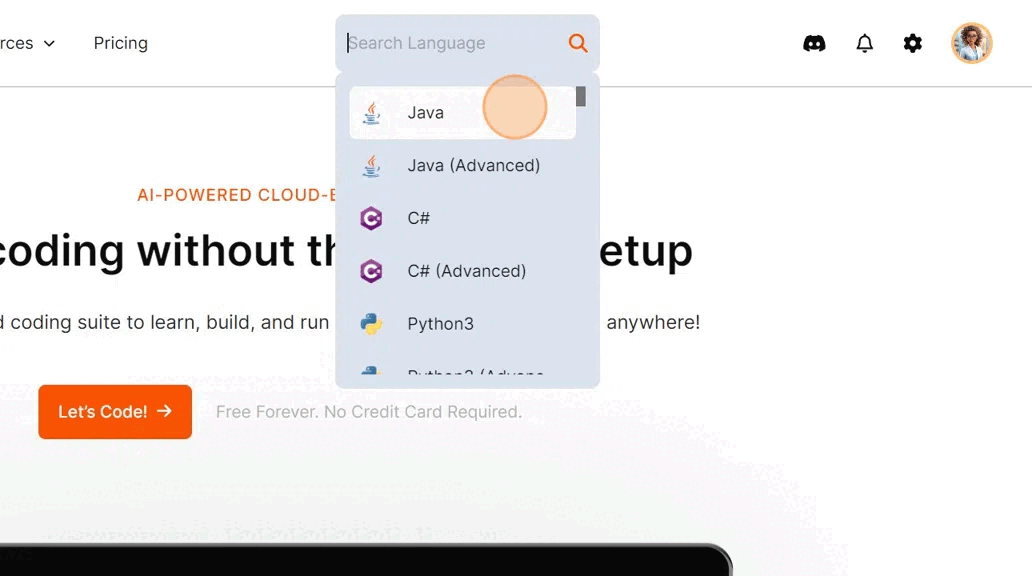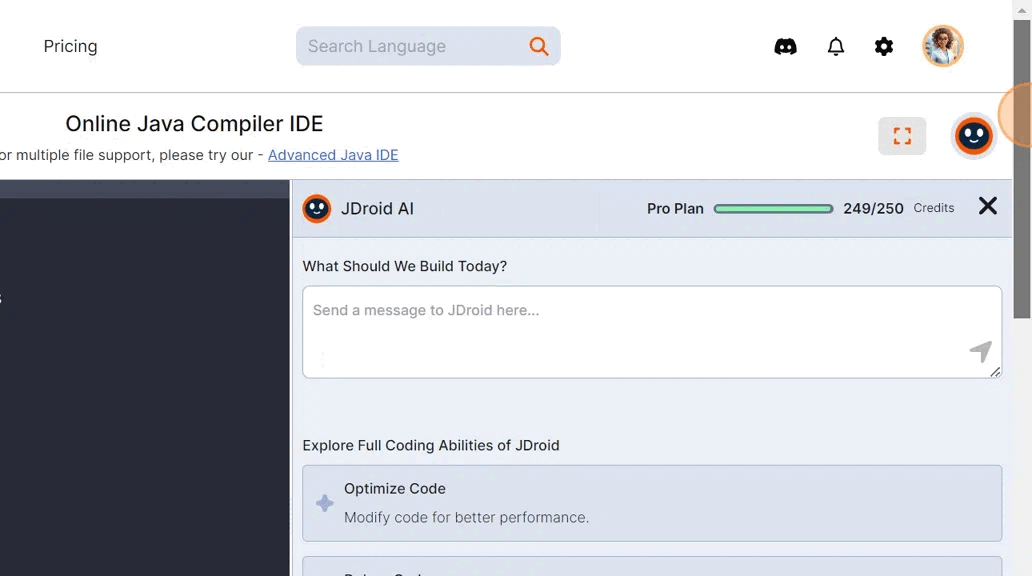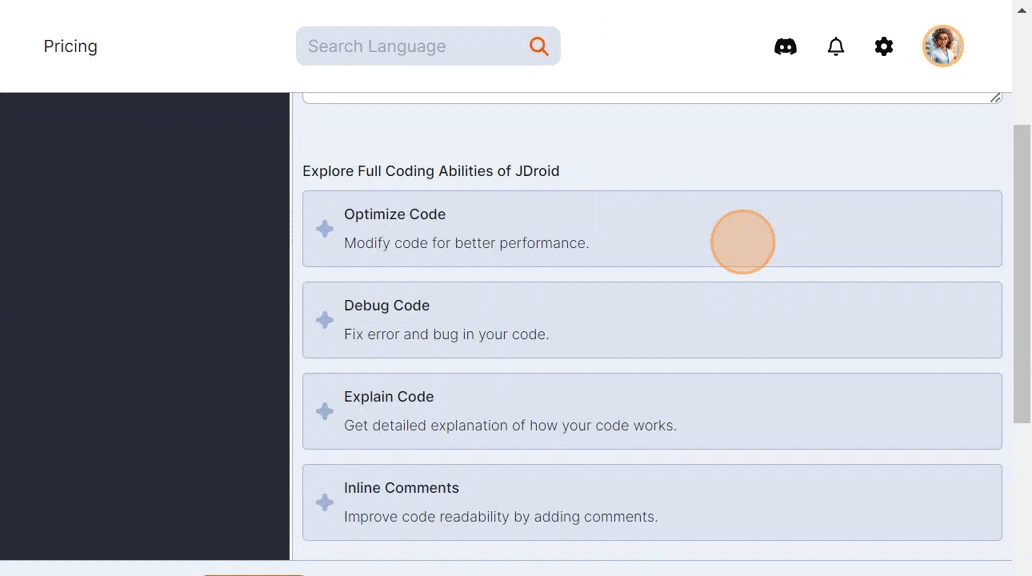
Important note:
When you opt for the explain code feature, it will only **explain the code in the IDE. ** If you need to explain a different code snippet, save the code you have in the IDE, paste the new snippet you wish to explain in the code editor, and select the explain code option. Refer to this documentation to understand how to save your code in the IDE.
How ‘explain code ’ works?
The explain code feature, when selected, gives a detailed code explanation of your logic and errors. We’re using a sample template code on simple addition on the JAVA compiler IDE to show how optimizing code works. 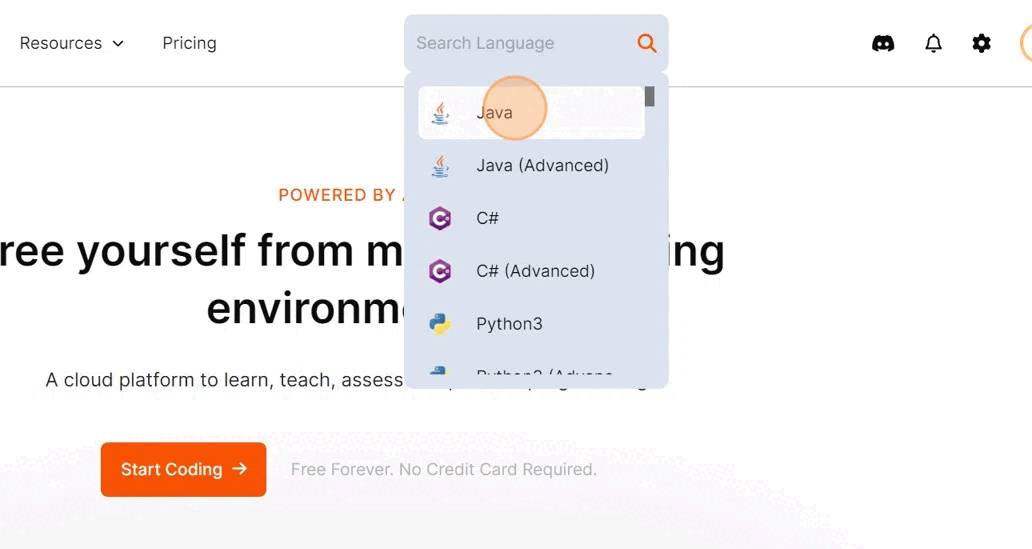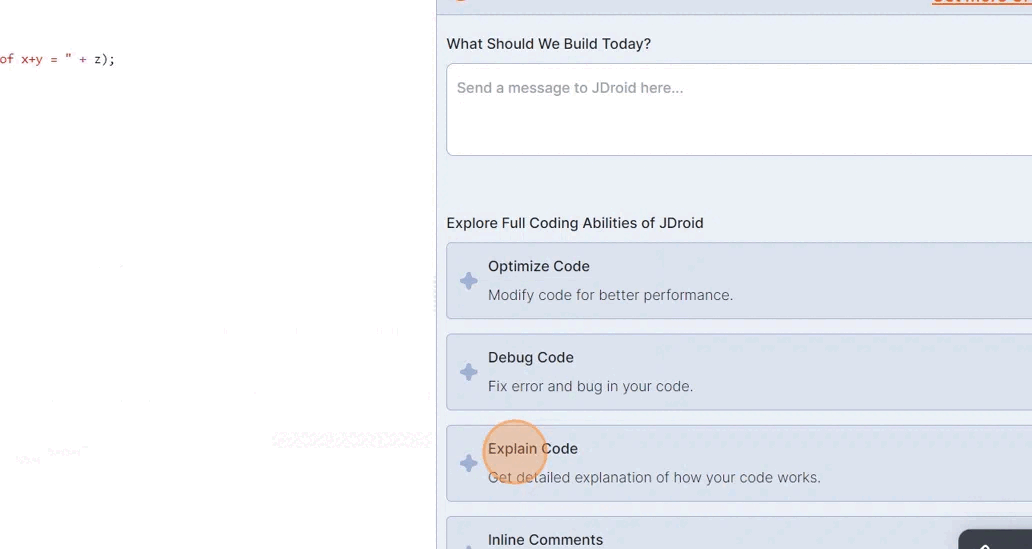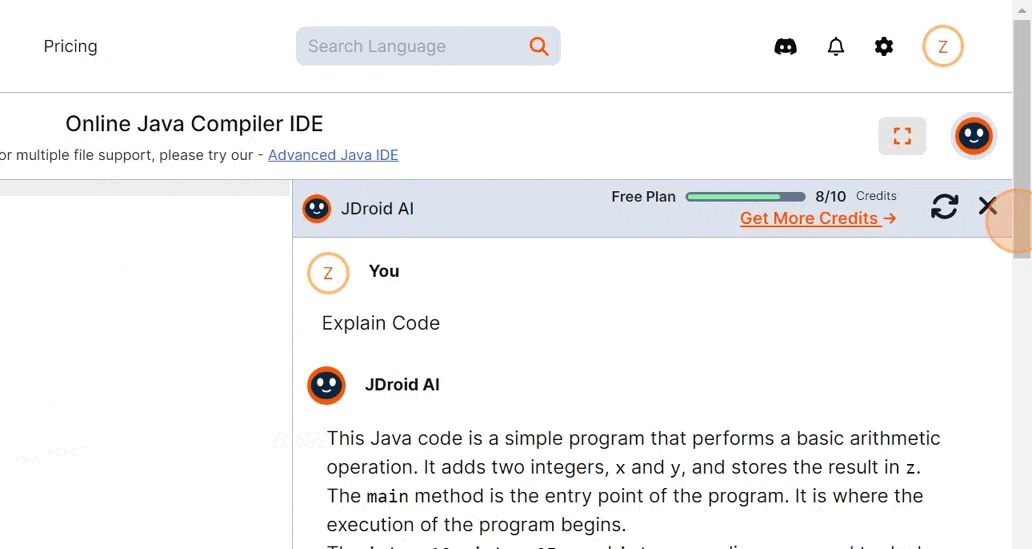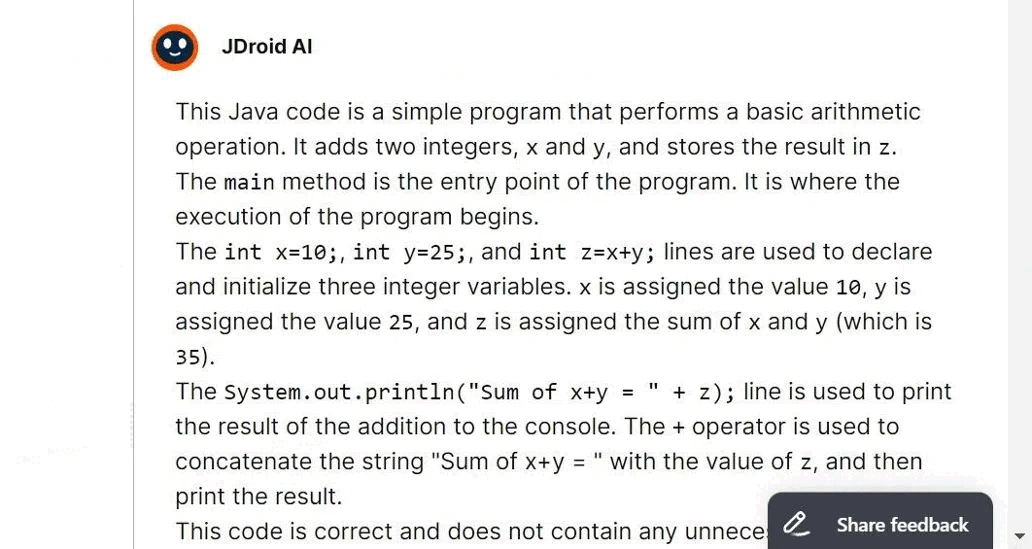 Here’s the sample template to try:
Here’s the sample template to try:
public class MyClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x=10;
int y=25;
int z=x+y;
System.out.println("Sum of x+y = " + z);
}
}
You can select the language you wish to code in, write or generate code using JDroid AI, and then select the explain code option. To understand how the generate new code feature works, read this documentation. If you generate code using JDroid, please paste it into the IDE so you don’t waste credits or encounter errors. Here’s the explanation given by JDroid:
This Java code is a simple program that performs a basic arithmetic operation. It adds two integers, x and y, and stores the result in z.
The main method is the entry point of the program. It is where the execution of the program begins.
The int x=10;, int y=25;, and int z=x+y; lines are used to declare and initialize three integer variables. x is assigned the value 10, y is assigned the value 25, and z is assigned the sum of x and y (which is 35).
The System.out.println("Sum of x+y = " + z); line is used to print the result of the addition to the console. The + operator is used to concatenate the string "Sum of x+y = " with the value of z, and then print the result.
This code is correct and does not contain any unnecessary, incorrect, or missing parts. It performs the required arithmetic operation and prints the result.
Note: The main method is a special method in Java that is used to start the execution of the program. It must be declared public, static, and void. The main method must be declared in a class, and it must be named exactly as main. The main method must be passed a single argument, which is an array of strings. The main method is where the program starts executing.
Example prompts to try
Here are sample code snippets you can ask JDroid AI to explain. The samples provided are in JAVA, so you must use the JAVA IDE.
Sample code that counts vowels and consonants
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello, World!";
str = str.toLowerCase();
int vowels = 0;
int consonants = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if(ch == 'a' || ch == 'e' || ch == 'i' || ch == 'o' || ch == 'u') {
vowels++;
} else if(ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
consonants++;
}
}
System.out.println("Number of vowels: " + vowels);
System.out.println("Number of consonants: " + consonants);
}
}
Sample to-do list code
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TodoList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> tasks = new ArrayList<String>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (True) {
System.out.println("1. Add Task");
System.out.println("2. Remove Task");
System.out.println("3. View Tasks");
System.out.println("4. Exit");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Enter task:");
scanner.nextLine();
String task = scanner.nextLine();
tasks.add(task);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Enter task number to remove:");
int index = scanner.nextInt();
tasks.remove(index - 1);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Tasks:");
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.size(); i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + ". " + tasks.get(i));
}
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Exiting...");
System.exit(0);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid choice. Please try again.");
break;
}
}
}
}
Things to consider while using explain code
JDroid AI is still learning and can produce wrong results, especially if:
- The code you ask JDroid to explain is not pasted in the IDE
- You’re using complex or new languages like Befunge,Cow,Brainfuck,Intercal, etc.
- The code you ask it to explain is very complex. This is a rare event, but it’s a possibility.
Need support?
If you encounter any issues with our ‘explain code’ feature or need more help, please submit this form or email hello@jdoodle.com. Our support team will respond as soon as possible.
